Rock Roller Bit is widely used in oilfields and ungroudwater well drilling. Compared with PDC oil bit and DTH bit, it has it's unique and irreplaceable working characteristics. Tricone Drill Bit developed since 1930's last century,is a big improvement compared with the two-cone bits.because of its versatility and drilling performance,nowadays it's still one of the main rock drilling bits.
Roller cone bits have cutters or cones with steel tooth or tungsten carbide inserts around them.As the drill string is rotated,the bit cones roll along the bottom of the borehole in a circular motion.As they roll,new teeth come in contact with the bottom of the hole,chipping the formation below and around the bit tooth.Air or drilling fluid life the crushed rock chips from the bottom of the hole and up the annulus. As rotation continues,another tooth makes contact with the bottom of the hole and creates new rock chips,thus,the process is continuous.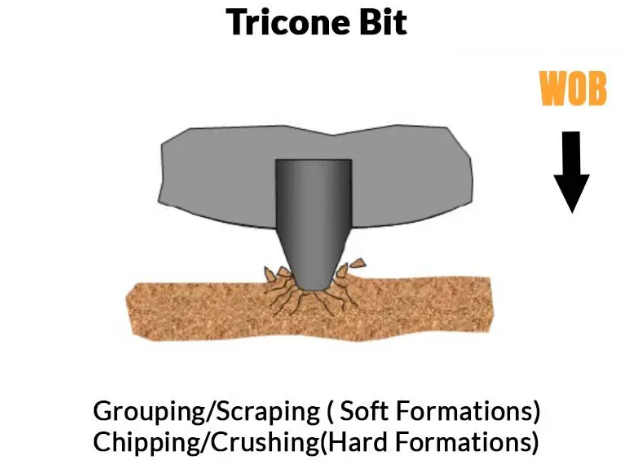
There are two typical types of tricone bits. It’s TCI(tungsten carbide insert) bits and MT(milled tooth)bits. Under the condition of different and complicated rock formations, there must be a perfect tricone bit suitably used for soft,medium and hard rock layers. Concerning this condition, every tricone bit has its own IADC code. It’s very important to be informed of drilling formation type when we select a best suitable tricone bit.

TCI tricone rock bits are famous for its wear-resisting and high strength tooth mertial which is more better than steel tooth bit. when drilling very complicated and changing formation,TCI tricone bit can provide excellent drillability.It's made by forging procedure and the Surface of bit covered with tungsten carbide profection to keep it from surface damage and heat. Rubber or metal sealed bearing system determines its long time working .
IADC 437 Soft Formation The 437 tci bits are used to drill low compressive strength,very soft formations .TCI bits maximize the use of bothconical and chisel tungsten carbide inserts of large diameters and high projection.This cutting structure design,combined with maximum cone offset,results in high bit penetration rates .The deep intermesh of cutter rows prevents bit bailing in sticky formations.
IADC 517 Medium Formation The 517 features aggressive chisel tungsten carbide inserts on the heel rows and inner rows.This desing provides a fast drilling rate and added cutting structure durability in medium-to medium hard formations .The HSN rubber o-ring provides adequate sealing for bearing durability.
IADC 617 Medium-Hard Formation The 617features robust chisel tungsten carbide inserts on the heel row and conical on the inner rows.This design provides a fast drilling rate and added sutti8ng structure durability in medium to medium hard formations .The HSN rubber o-ring [rovodes adequate sea;omg fpr bearomg dirability.
IADC 637 Hard Formation The 637 features can be used to drill hard and abrasive formations .Wearresistant tungsten carbide inserts are used in the outer rows to prevent loss of bit gauge.Maximum numbers of bemisphericalshaped inserts are used in all rows to provide cutter durability and long life.
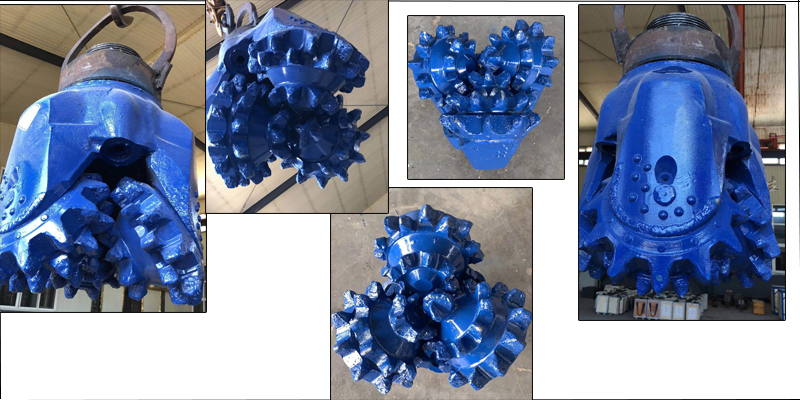

Milled tooth tricone bits are famous for its high speed drilling penetration(high RPM) in soft formation like sandstone,shale,halite,etc. It's made by casting procedure and the Surface of bit covered with tungsten carbide protection to keep it from wearing.
IADC 114. 115.116.117 Soft formation The 114-117 bits are used to drill low-compressive strength,soft formations. Long projection tooth lengths are used on high offset cones to provide the greatest penetration rates possible. Wear-resistant hard facing is used to control tooth wear.On the softest bi types this hard facing completely covers the bit teeth.
IADC 124.125.126.127 Medium formation Medium formation with high-compressive strength and high drillability. Such assandstone, anhydrite, salt, shale, limestone.
IADC 134.135.136.137 Medium soft formation Formations with low compressive strength, such as shale, anhydrite, sand and so on for soft formation IADC 216.217 Medium hard formation The 216-217 bit are always used to Soft to medium formations with low-compressive strength, such as shale, anhydrite, sand and so on for soft formation.
Nowadays,Tricone roller bits are widely used in the industries of Gas Wells,Oil Wells, Water Wells,Mining, Environmental,Geothermal, Blast Holes,Construction,Exploration,Etc.
What Cause Tricone Drill Bit Broken
Cause:drop drill string
Hitting a ledge
Cone interferance
Bearing failure
Resulting in cracks/broken cone
- Cone Interferance
Cause:bearing failure
Pinched bit
Cone interferance
Low quality/material
- Cored
Cause: excessive WOB
Cone shell erosion
Abrasive formation
Improper break-in
Improper bit selection
Junk in hole
- Chipped teeth
Cause:junk in hole
Rough drilling
Normal wear
Cone interference
High impact loading
Weak design/material
- Eroded cone
Cause:abrasive formation
Excessive WOB
Poor solids control
Off center wear
High velocity fluid erosion
Weak design/material
- Cracked cone
Cause: dropped drill string
Over heating
Cone interference
Junk at bottom of hole
Hitting a ledge on bottom
Hydrogen sulfide embrittiement
- Junk damage
Cause: junk in hole
Junk from the drill string
Junk from the drill bit
Junk from a previous run
- Heat checking
Cause:reaming under gage hole
Inserts being dragged
Heated inserts
Hard and abrasive formation
- Lost teeth
Cause:cone cracking
Cone shell wear/erosion
Weak material/design
Hydrogen sulfid cracks
- Rounded gage
Cause:abrasive formation
Excessive RPM
Reaming under gage hole
- Tracking
Cause:formation changes(brittle to plastic)
Excessive hydrastatic pressure
Improper WOB/RPM combination
- Shirttail damage
Cause:poor hydralics
High angle well bore
Pinched bit
Reaming under gage hole
- Flat crested
Cause:low WOB,high RPM
Drilling parameters
Formation
Hard-facing
Normal wear
- Worn teeth
Cause: normal wear
 Urumqi Siruite Mechanical Equipment Co.,Ltd
Urumqi Siruite Mechanical Equipment Co.,Ltd
